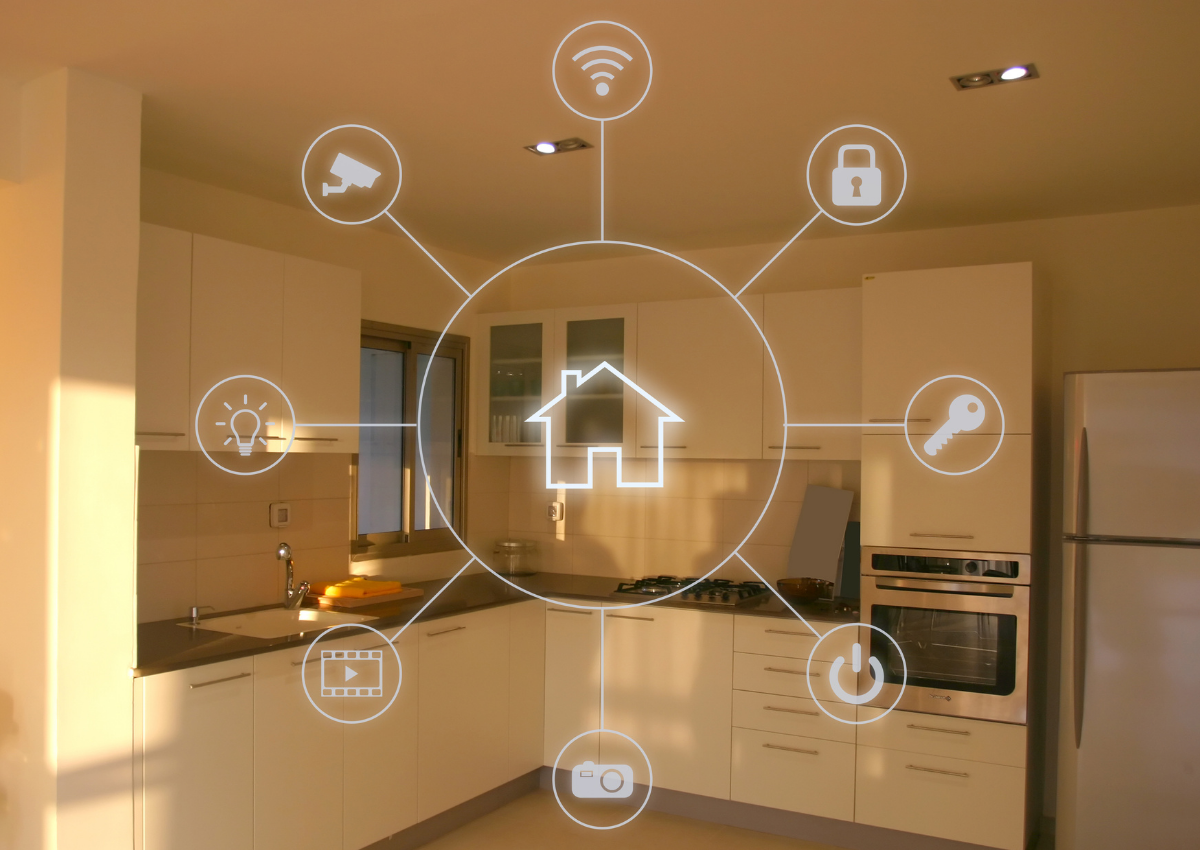
Industry 4.0 is a revolutionary concept, ushering in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. It embodies a profound shift towards interconnectivity, automation, machine learning, and the utilization of real-time data. Industry 4.0 goes beyond traditional manufacturing and production approaches by synergizing physical operations with smart digital technology, big data analytics, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). This transformative paradigm empowers companies to create a more interconnected and efficient ecosystem, focusing on manufacturing excellence and streamlined supply chain management.
Amidst diverse industries and organizations, the quest for connectedness and access to real-time insights remains a common challenge. The dynamic nature of business demands seamless integration across processes, partners, products, and people, which Industry 4.0 readily addresses. By embracing the principles of Industry 4.0, companies can optimize their operations, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge in a world shaped by advanced technologies and data-driven decision-making. In this post, learn the essence of Industry 4.0, exploring its core elements and practical applications across various sectors. Discover how Industry 4.0 reshapes industries and propels us into a more connected and intelligent future.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is a term that originated in Germany and was introduced at the Hannover Messe trade fair in 2011. It represents the fourth wave of industrial revolutions, following the earlier transformations by mechanization, mass production, and digital technology. Industry 4.0 is driven by the fusion of cutting-edge technologies, data analytics, and smart manufacturing to create a highly interconnected and efficient ecosystem.
Key Components of Industry 4.0
Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT forms the backbone of Industry 4.0. It involves a vast network of interconnected devices, sensors, and machines that collect and exchange data in real time. These devices can be anything from production equipment and wearables to logistics systems and smart appliances.
Big Data and Analytics
Industry 4.0 generates immense data from various sources. Big data analytics plays a pivotal role in processing and deriving actionable insights from this data. These insights drive informed decision-making, predictive maintenance, and continuous process improvements.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is at the heart of Industry 4.0’s autonomous capabilities. Machine learning algorithms and AI-powered systems enable machines to learn from data, optimize processes, and make intelligent decisions without human intervention.
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
CPS represents the integration of physical machines with digital systems. This enables real-time data sharing, feedback loops, and the capability for machines to adapt to changing conditions, enhancing overall efficiency and productivity.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing enables the creation of complex and customized products through layer-by-layer printing of materials. It revolutionizes traditional manufacturing processes, reduces waste, and offers new possibilities for design and prototyping.
Cloud Computing
The cloud provides a scalable and secure platform to store and access vast amounts of data from anywhere. It enables seamless collaboration, remote monitoring, and real-time data sharing among stakeholders.
How Does Industry 4.0 Work?
Industry 4.0 is driven by digital technologies’ convergence and integration into various industrial processes. The working principles of Industry 4.0 are as follows:
Interconnectivity and Data Sharing
Industry 4.0 relies on connecting devices, systems, and people seamlessly. IoT-enabled sensors and devices collect real-time data from machines and processes. This data is then shared through a standard communication protocol, enabling the entire production line to be interconnected and responsive.
Real-Time Data Analysis
The data collected from interconnected devices is analyzed using advanced analytics and AI algorithms. Real-time data analysis allows for quick identification of inefficiencies, predictive maintenance, and immediate responses to changing conditions.
Autonomous Systems
AI and machine learning algorithms empower machines to make decisions and take actions based on data analysis. Autonomous systems reduce human intervention, increase efficiency, and enable continuous optimization.
Smart Factories
Industry 4.0 introduces the concept of smart factories, where production processes are highly automated and digitized. Smart factories use CPS to create a flexible and agile manufacturing environment where machines can self-optimize and adapt to changing demands.
Personalization and Customization
Industry 4.0 enables mass customization and personalized products. With 3D printing and advanced manufacturing technologies, companies can create unique products tailored to individual customer preferences.
Resource Efficiency and Sustainability
Industry 4.0 promotes resource efficiency and sustainability by optimizing processes and reducing waste. Real-time data monitoring allows for better energy management, reduced material usage, and minimized environmental impact.
Practical Applications of Industry 4.0
Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 revolutionizes traditional manufacturing processes by introducing smart factories, where machines, equipment, and logistics systems communicate and work together seamlessly. It allows for predictive maintenance, just-in-time production, and improved product quality.
Supply Chain Management
Industry 4.0 optimizes supply chain operations through real-time inventory, shipments, and logistics tracking. It enhances transparency, reduces lead times, and minimizes stockouts.
Healthcare
Industry 4.0 enables wearable devices, remote patient monitoring, and AI-powered diagnostics in the healthcare sector. These technologies improve patient care, enable early detection of diseases, and enhance treatment outcomes.
Energy and Utilities
Industry 4.0 plays a crucial role in smart energy management and grid optimization. It enables real-time energy consumption monitoring, facilitates demand response, and promotes renewable energy integration.
Transportation and Logistics
Industry 4.0 enhances transportation and logistics operations through autonomous vehicles, real-time tracking, and route optimization. It reduces delivery times, minimizes fuel consumption, and improves overall efficiency.
Retail
Industry 4.0 enables personalized customer experiences through AI-driven recommendations and customized products in the retail sector. It also enhances inventory management and supply chain visibility.
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 represents a groundbreaking era of innovation and technological advancement, transforming industries and societies. Its core components, including IoT, big data, AI, and CPS, drive new opportunities for efficiency, sustainability, and customization. By leveraging Industry 4.0 technologies, businesses can enhance their operations, improve customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge in the dynamic global market. Embracing Industry 4.0 is not just a technological shift but a strategic imperative to thrive in the digital age and shape the future of the industry and beyond.
Also Read: